what is gas turbine ?
introduction
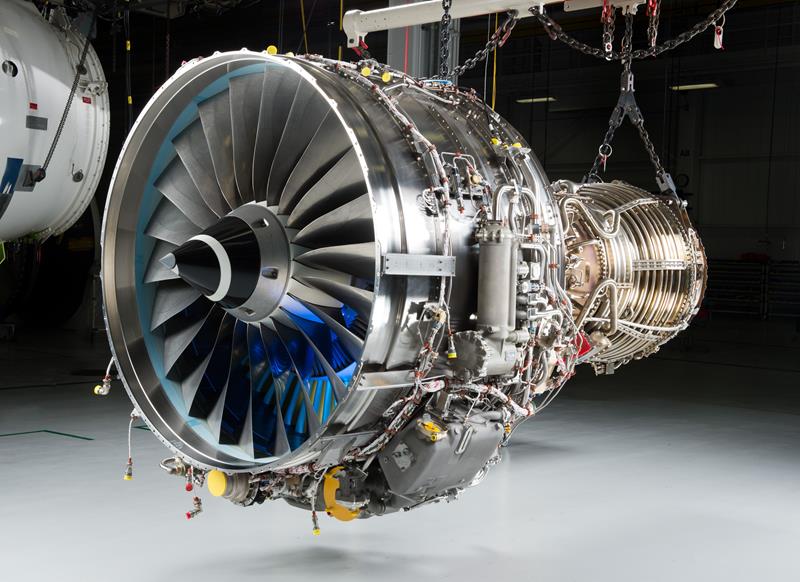
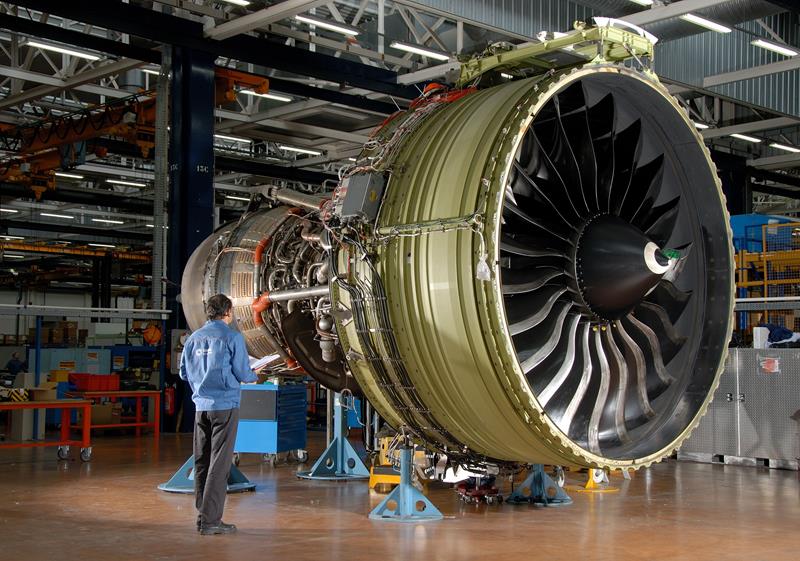
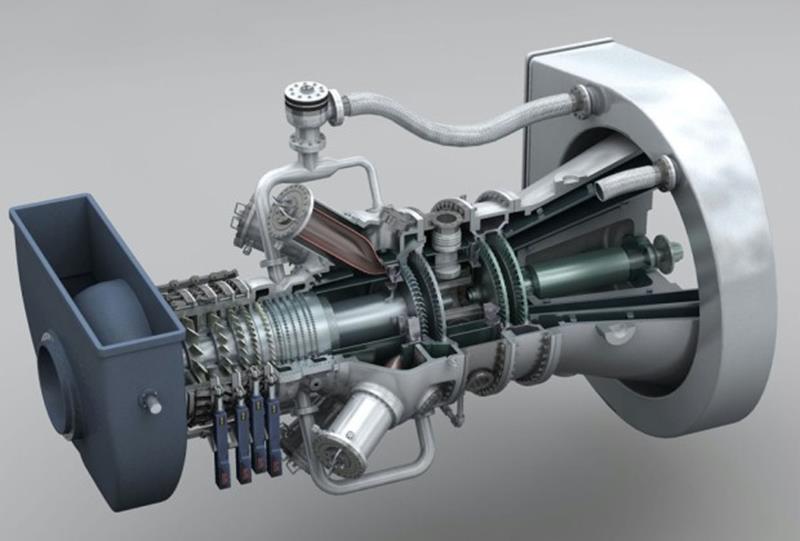
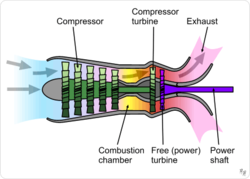
Gas Turbine is an internal combustion engine of rotary machines that operates on the energy of combustion gases. It is mainly used in power plants, but helicopter engines, passenger aircraft engines, warplane engines and ship turbine engines are also types of gas turbines.
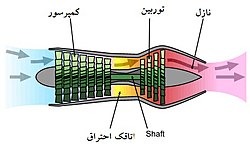
Each gas turbine includes a compressor to compress the air, a combustion chamber to mix the air with the fuel and ignite it, and a turbine to convert the internal energy of the hot and compressed gases into mechanical energy. Some of the mechanical energy generated in the turbine is spent on spinning the compressor itself, and the rest of the energy, depending on the application of the gas turbine, may spin the electric generator (turbogenerator), accelerate the air (turbojet and turbofan) either directly (or after a change). Rotation speed by gearbox) to be used in the same way (Turboshaft, Turboprop and Turbofen).
Types of gas turbines
Industrial gas turbines to generate electric power
Industrial gas turbines for the production of electric power, also called gas turbogenerators, are gas turbines by which the power generated is transmitted directly to the generator directly or after a change in the speed of the gearbox, where it is converted into electric potential energy. This type of gas turbine can be in the form of a simple cycle (Single Cycle) or a combined cycle power plant (Combined Cycle). In the simple cycle mode, the exhaust gases from the turbine, which can have a temperature of up to 600 degrees Celsius, enter directly into the air and the remaining energy is wasted; But in the combined cycle mode, one or two gas turbines are coupled to a steam turbine, and the exhaust gases from the gas turbine in a section called the recovery boiler convert the water returning from the condensate of the steam turbine, which is compressed by the pump, into steam. As a result, in the combined cycle mode, the energy in the exhaust gases from the gas turbine exhaust is used and the steam turbine boiler produces water vapor without the need for fuel; Therefore, using this method, the cycle efficiency increases. Turbogenerators can also be used to generate electricity and heat at the same time (cogeneration), in which the exhaust gas is used to produce hot water or hot air for buildings and factories.

Gas turbines for mechanical energy production
These types of gas turbines, which include turbochargers and turbopumps, are gas turbines in which the energy produced by the turbine is used to turn a compressor (to compress a gaseous substance) or a pump (to increase the pressure of a liquid).
Jet engines
Jet engines are a type of engine that uses acceleration and discharge of fluid to propel it according to Newton’s third law. Two types of jet engines, turbojets and turbofans, include gas turbines and are in fact a type of gas turbine.
Turbojets are a type of gas turbine in which all the energy produced in the turbine is spent on the rotation of the compressor and the hot air leaving the turbine, after passing through a nozzle, accelerates and leaves the end as a fluid jet at high speed.
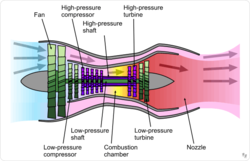
Turbofans are another type of jet engine in which, unlike turbojets, not all of the air entering the engine passes through the compressor, combustion chamber, and turbine, but most of the air, after passing through one or two rows of large blades called fans, passes through the duct. They move around the compressor and come out of a nozzle. A small amount of air passes through the compressor, ignites and spins the turbine. The energy generated by the turbine is used to turn the compressor and fan; Therefore, in this type of jet engine, its propulsion is caused by both the output fluid jet and the fan rotation. The thermal efficiency of tubofen at higher speeds than the speed of sound (Mach less than 1), which is the speed of passenger aircraft, is higher than that of turbojets. Thus, after the invention of turbofan, they were gradually used in passenger aircraft, and today the engine of most passenger aircraft is turbofan.
Turboshafts
Turboshaft is the engine of most helicopters today, which is used in addition to helicopters in ships, tanks, hovercrafts and some boats. Gas turbines are used in turbochargers, similar to turbochargers and turbopumps, to generate mechanical energy. The difference is that in turboshaft, the mechanical energy produced is not used to turn the compressor or pump. In these engines, the energy output from the turbine, after reducing the rotational speed in the gearbox, causes the propeller of a helicopter, ship or hovercraft to rotate.
Turboshaft engines are two-stroke. The first shaft, which includes the compressor, combustion chamber, and high pressure turbine, is called the compressor shaft or gas generator shaft. The second shaft, which includes the Low Pressure Turbine, transmits mechanical power to the gearbox to be consumed after reducing the speed. This shaft is called the Power Shaft. All the power generated by the high-pressure turbine is used to spin the compressor and create compressed air, hence the term shaft generator. Production power is transmitted to the consumer by a low pressure turbine.
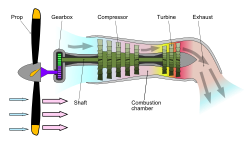
Turbopropers
Turboprop is a type of air engine commonly used in small, low-speed aircraft. This type of engine is similar to a turboshaft and uses a turbine shaft to turn the propeller and propel it. Turboprops perform better at low speeds than turbofans and turbojets, but at higher speeds, their efficiency decreases and their noise increases.
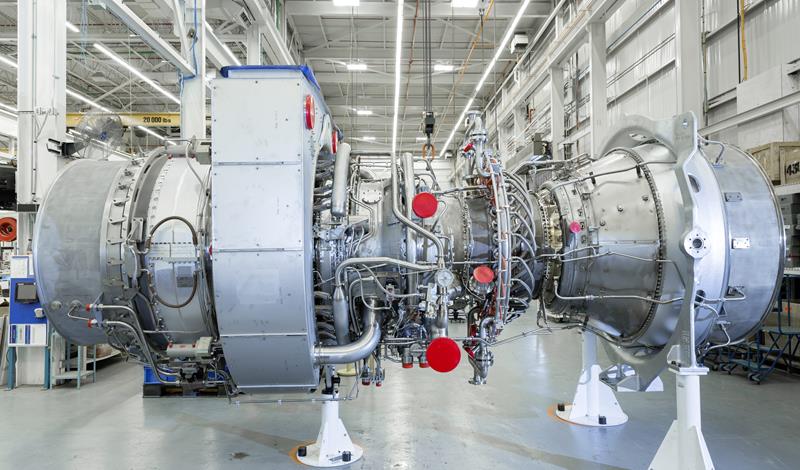

The main manufacturers of gas turbines
Today, the global companies producing gas turbines in the world are:
GE
Siemens
Alstom
Ansaldo Energy
Rolls-Royce Holding
Perth & Whitney
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI)
Advantages and disadvantages of gas turbines Gas turbines
Power to weight ratio: Gas turbines are smaller than reciprocating engines with the same power.
Very low start-up time compared to thermal turbines
Less vibration: Due to moving in one direction, the vibration of gas turbines is less than reciprocating engines.
Less moving parts than reciprocating engines.
Lower lubrication cost
Disadvantages of gas turbines
Expensive
High working temperature
Less efficiency than idle reciprocating engines
Improper operation in load oscillation conditions